-
Category Management
Category Management
Partnership between Retailers and Manufacturers
Category Managers and Trade Marketers
Trade Marketing
Origins of Category Management
Trade Formats
Categories
Category Roles
Category Strategies
Review
Retail Mix
Price
Promotions and In-Store Media
Space Management
Execution
Benefits of Category Management
Developments in Retailing
- Retail Tracking
- Sales and Distribution
- Retail Analytics
- Category Management
- Marketing Education
- Is Marketing Education Fluffy and Weak?
- How to Choose the Right Marketing Simulator
- Self-Learners: Experiential Learning to Adapt to the New Age of Marketing
- Negotiation Skills Training for Retailers, Marketers, Trade Marketers and Category Managers
- Simulators becoming essential Training Platforms
- What they SHOULD TEACH at Business Schools
- Experiential Learning through Marketing Simulators
-
MarketingMind
Category Management
Category Management
Partnership between Retailers and Manufacturers
Category Managers and Trade Marketers
Trade Marketing
Origins of Category Management
Trade Formats
Categories
Category Roles
Category Strategies
Review
Retail Mix
Price
Promotions and In-Store Media
Space Management
Execution
Benefits of Category Management
Developments in Retailing
- Retail Tracking
- Sales and Distribution
- Retail Analytics
- Category Management
- Marketing Education
- Is Marketing Education Fluffy and Weak?
- How to Choose the Right Marketing Simulator
- Self-Learners: Experiential Learning to Adapt to the New Age of Marketing
- Negotiation Skills Training for Retailers, Marketers, Trade Marketers and Category Managers
- Simulators becoming essential Training Platforms
- What they SHOULD TEACH at Business Schools
- Experiential Learning through Marketing Simulators
Category Roles
| Destination: To be the primary category provider and help define the retailer as the store of choice by delivering consistent, superior target customer value. |
|---|
| Routine: To be one of the preferred category providers and help develop the retailer as the store of choice by delivering frequent, competitive target consumer value. |
| Occasional/Seasonal: To be a major category provider, help reinforce the retailer as the store of choice by delivering frequent, competitive target consumer value. |
| Convenience: To be a category provider and help reinforce the retailer as the full-service store of choice by delivering good target consumer value. |
Exhibit 33.7 Category roles (Source: TPG).
The importance of a category is dependent on two key factors — strategic fit and category attractiveness.
Strategic Fit
Strategic fit is a function of how the category relates to the chain’s identity and value proposition. Is there high synergy between the category and the chain? Is the category well aligned with the chain’s purpose and identity? Is it important to target shoppers?
Two measures that help assess the strategic fit with shoppers are chain loyalty and propensity. (Refer to Chapter Retail Analytics for details).
Another relevant metric is the Fair Share Index: $$\large{\text{Fair Share Index} = \frac{\text{Value Share of Chain in Category}}{\text{Value Share of Chain in All categories}}}$$
The fair share index reflects the importance of the category to the retail chain, in terms of the chain’s contribution to category sales.
Category Attractiveness
Category attractiveness is a function of its size and growth rate in terms of volume, value, and profitability.
Category Roles
The Partnering Group (TPG) advocated four basic roles — destination, routine, convenience and occasional/seasonal. As described in Exhibit 33.7, these roles establish a category’s place within the chain’s portfolio and form the basis for the allocation of resources.
Destination categories rank high on strategic fit as well as category attractiveness. They are central to the chain’s identity and of strategic importance to their business.
Typically for mainstream supermarkets the destination categories tend to be the major food and personal care categories in the country. For instance, milk, soft drink, beer, cooking oil and rice, in the context of Asia.
Sometimes the destination category may distinguish a supermarket chain from other supermarkets. For example, wine is a destination category at Cold Storage, an upmarket supermarket chain that targets expatriates and affluent residents in Singapore. It is also the biggest packaged foods category at the chain; this even though wine is a relatively small category in the country.
For personal care chains like Watsons, beauty and personal care categories like facial care, skin care and hair care would be considered destination category.
Routine categories rank medium to high on strategic fit and category importance. Their presence and offering also has some bearing on store selection and they reinforce the banner’s identity and image, but not to the same extent as destination categories.
Breakfast cereals and pet foods are examples of routine categories in Asian supermarkets where the proportion of shoppers who purchase these categories is relatively low compared to many Western countries.
Supermarket chains often stock a limited range of magazines and newspapers for convenience, but usually no books. Some chains however made an exception for the exceedingly popular Harry Potter series, at the time the books were released. This served to excite young shoppers and provided convenience to them and their parents.
Convenience categories such as books and magazines in supermarkets, or snacks and beverages in personal care stores, rank low on strategic fit and category importance. Their presence provides for one-stop shopping convenience for the chain’s shoppers.
Seasonal or occasional categories refer to product categories that are specifically associated with particular seasons, holidays, or special occasions. These categories are characterized by their temporary nature and increased demand during specific times of the year. Examples of include New Year’s greeting cards, holiday decorations, Halloween costumes, Christmas pudding and roast turkey, Chinese New Year snacks, and categories like sun block, insecticides, summer apparel and winter clothing.
Previous Next
Use the Search Bar to find content on MarketingMind.
Online Apps to train Category Managers
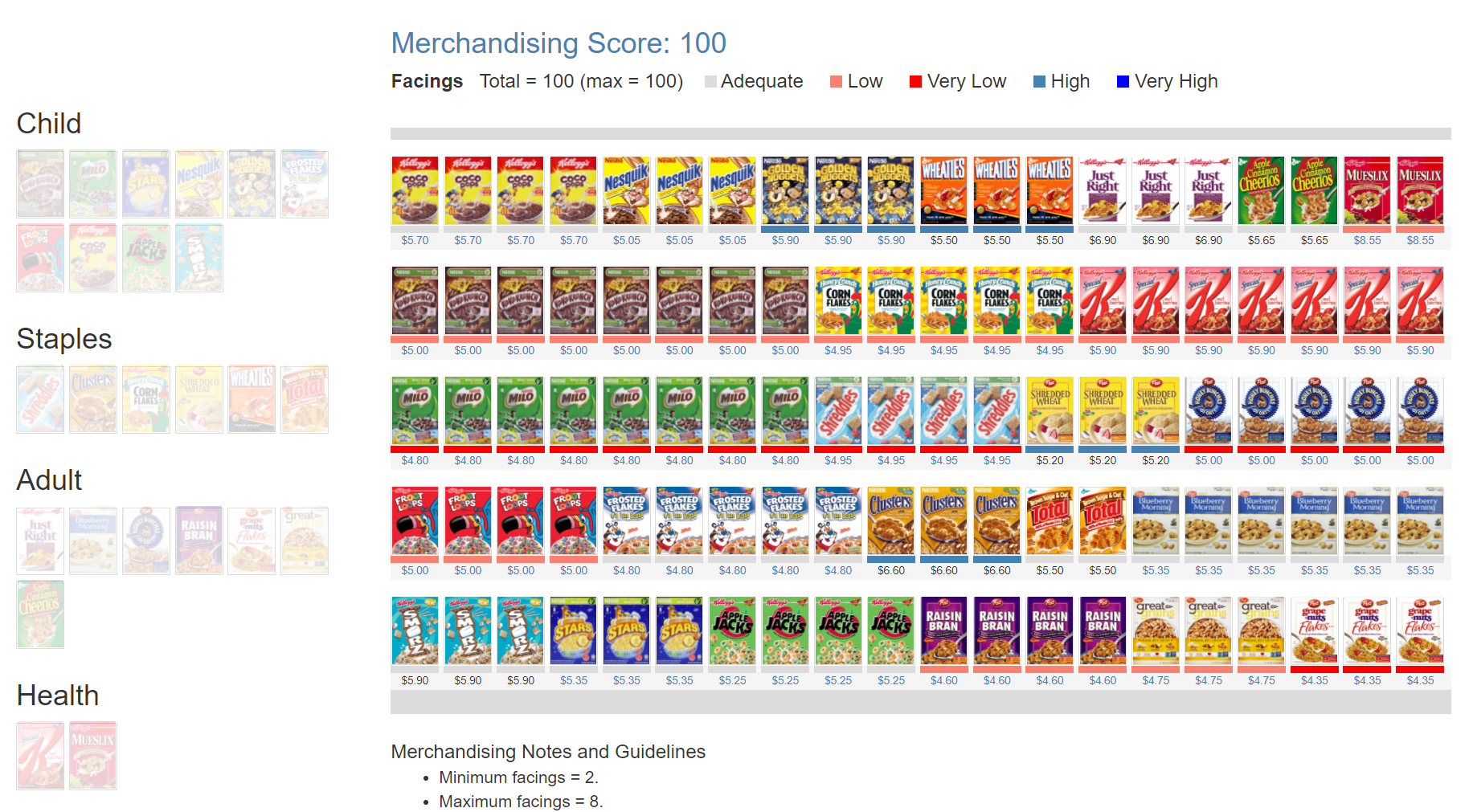
The Plannogrammer is an experiential learning facility for category managers, trade marketers, and retailers in consumer markets. Ideally suited for hybrid learning programmes, Plannogrammer imparts hands-on training in the planning and evaluation of promotions and merchandising.
It supports a collection of simulation and analysis platforms such as Promotions and Space Planner for optimizing space and promotions, Plannogram for populating shelves and merchandising, a Due To Analysis dashboard that decomposes brand sales into the factors driving sales, and a Promotion Evaluator to evaluate the volume, value and profit impact of promotion plans.
Contact | Privacy Statement | Disclaimer: Opinions and views expressed on www.ashokcharan.com are the author’s personal views, and do not represent the official views of the National University of Singapore (NUS) or the NUS Business School | © Copyright 2013-2026 www.ashokcharan.com. All Rights Reserved.





